Difference between revisions of "WormMine"
Mzarowiecki (talk | contribs) (→Links) |
Mzarowiecki (talk | contribs) (→Links) |
||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
= Links = | = Links = | ||
[http://intermine.wormbase.org/tools/wormmine/begin.do WormMine] | [http://intermine.wormbase.org/tools/wormmine/begin.do WormMine] | ||
| + | |||
[https://github.com/WormBase/intermine WormMine Github] | [https://github.com/WormBase/intermine WormMine Github] | ||
| − | [[UserGuide:WormMine|User Guide] | + | |
| + | [[UserGuide:WormMine|User Guide]] | ||
= Logging in as admin = | = Logging in as admin = | ||
Latest revision as of 16:16, 15 October 2020
Contents
Current status
|
ONLINE |
Links
Logging in as admin
These specific URLs must be used since the admin account is a WormMine, not Google, account.
Login URL: http://www.wormbase.org/tools/wormmine/login.do
Logout URL: http://www.wormbase.org/tools/wormmine/logout.do
Find the admin account username and password by executing this search in your wormbase.org account:
subject:[ WormMine ] Important update on status and curator action
This account is needed to publish templates to the front page.
New data wishlist
| Name | Where is the data? |
|---|---|
| Orthology | ACeDB gene class (Ortholog and Ortholog_other tags) and there is also a OICR created flatfile) |
| Interaction | AceDB interaction class |
| Transgene | Transgene AceDB class |
| variation coordinates | gff3, type SNP or SNP |
| Disease data | In AceDB class ?Gene, Import all data under the Disease_info tag |
| Motif Titles | In the "Title" tag of ?Motif |
Data contained in WormMine
This lists all data sources contained in WormMine
Refer to species list:
| taxonId | species |
|---|---|
| 6253 | Ascaris suum |
| 6279 | Brugia malayi |
| 6326 | Bursaphelenchus xylophilus |
| 96668 (860376 according to NCBI) | Caenorhabditis angaria |
| 135651 | Caenorhabditis brenneri |
| 6238 | Caenorhabditis briggsae |
| 6239 | Caenorhabditis elegans |
| 281687 | Caenorhabditis japonica |
| 31234 | Caenorhabditis remanei |
| 6289 | Haemonchus contortus |
| 37862 | Heterorhabditis bacteriophora |
| 6305 | Meloidogyne hapla |
| 6306 | Meloidogyne incognita |
| 54126 | Pristionchus pacificus |
| 34506 | Strongyloides ratti |
| 6334 | Trichinella spiralis |
| Source | Description | Source | Species | Filters | Data mapping |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GO | Ontology terms and relationships comprising GO | GO project website (We should record the CVS revision number of the ontology file we use so we can perform data checks). | species neutral | ||
| GO Annotations | Relationships between Genes and GO | GO project website. | Caenorhabditis elegans | Removes all with first column = "UniProtKB" | |
| Genomic sequences | Fasta DNA sequences | WormBase FTP | All in species list | ||
| Protein sequences | Fasta peptide sequences | WormBase FTP | All in species list | ||
| Gene locations | Gene chromosomal coordinates | WormBase FTP GFF3 | All in species list | ||
| Transcript locations | Transcript chromosomal coordinates | WormBase FTP GFF3 | All in species list | ||
| CDS locations | CDS chromosomal coordinates | WormBase FTP GFF3 | NONE (locations load improperly) | ||
| Gene metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | query find Gene Live
|
LINK |
| Transcript metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | query find Transcript (Gene)
|
LINK |
| CDS metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | query find CDS Method="curated"
|
LINK |
| Variation metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Protein metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | Limited to these species,
|
LINK |
| Phenotype metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Expression Pattern metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Anatomy Term metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Expression Cluster metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Life Stage metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK | |
| Species data | Name and Taxon ID | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | Species list | LINK |
| RNAi metadata | Select fields extracted from Ace | AceDB XML dump | All in AceDB | LINK |
What is this data mapping?
A loading program plugin has been created for InterMine which extracts data embedded in XML files directly into an InterMine instance. Mapping files are used to configure this program and detail the AceDB XML dumps to InterMine translation. XPath is used to query the XML, and can be reviewed here.
Understanding our model
The data contained in WormMine follows a central model schema. This model should be understood sufficiently to be able to query the data and create templates.
This schema file contains all of the data types contained in WormMine, relationships between them, and each one's data fields.
How to read it
Looking at the protein class:
<class name="Protein" extends="BioEntity" is-interface="true">
<attribute name="molecularWeight" type="java.lang.Float"/>
<attribute name="md5checksum" type="java.lang.String"/>
<attribute name="length" type="java.lang.Integer"/>
<attribute name="geneName" type="java.lang.String"/>
<attribute name="primaryAccession" type="java.lang.String"/>
<reference name="sequence" referenced-type="Sequence"/>
<collection name="CDSs" referenced-type="CDS" reverse-reference="protein"/>
<collection name="genes" referenced-type="Gene" reverse-reference="proteins"/>
<collection name="transcripts" referenced-type="Transcript" reverse-reference="protein"/>
</class>
Line by line:
<class name="Protein" extends="BioEntity" is-interface="true">
extends="BioEntity": Protein is a child of BioEntity therefore it inherits BioEntity's data fields.
Protein's parent, BioEntity:
<class name="BioEntity" is-interface="true">
<attribute name="secondaryIdentifier" type="java.lang.String"/>
<attribute name="symbol" type="java.lang.String"/>
<attribute name="primaryIdentifier" type="java.lang.String"/>
<attribute name="lastUpdated" type="java.util.Date"/>
<attribute name="name" type="java.lang.String"/>
<reference name="organism" referenced-type="Organism"/>
<collection name="synonyms" referenced-type="Synonym" reverse-reference="subject"/>
<collection name="publications" referenced-type="Publication" reverse-reference="bioEntities"/>
<collection name="ontologyAnnotations" referenced-type="OntologyAnnotation" reverse-reference="subject"/>
<collection name="phenotypesObserved" referenced-type="Phenotype" reverse-reference="observedIn"/>
<collection name="phenotypesNotObserved" referenced-type="Phenotype" reverse-reference="notObservedIn"/>
<collection name="crossReferences" referenced-type="CrossReference" reverse-reference="subject"/>
<collection name="dataSets" referenced-type="DataSet" reverse-reference="bioEntities"/>
<collection name="locatedFeatures" referenced-type="Location" reverse-reference="locatedOn"/>
<collection name="locations" referenced-type="Location" reverse-reference="feature"/>
</class>
Protein contains copies of all these attributes, references, and collections for itself. If BioEntity inherits any fields itself, those are included as well.
<attribute name="primaryAccession" type="java.lang.String"/>: This creates an attribute of protein called primaryAccession (read primary accession) which is a string (word(s)). This line enables every protein object to hold a primaryAccession value in addition to any children which may inherit from it.
<reference name="sequence" referenced-type="Sequence"/>: This creates a reference named "sequence" to another data type, in this case Sequence. Only one sequence object can be referenced this way at a time. reverse-reference attributes may appear here, which matches the reciprocal relationship in the referenced type if one exists.
<collection name="CDSs" referenced-type="CDS" reverse-reference="protein"/>: CDSs collection. It can hold many references to CDSs, which in return are stored in the CDS "protein" (CDS.protein) field.
Using QueryBuilder
Use case: How do I find all proteins for a gene?
How are they intuitively connected? Genes are transcribed into transcripts which contain coding sequences which are translated into proteins. Keep this in mind while constructing a query.
- Select "Gene" in the box under "Select a Data Type to Begin a Query"
- Click "Select", or double click "Gene"
This list represents the Gene data available to display. Various fields can be chosen to be shown in the results table, links to other data types followed, and filters can be set to constrain the results.
Desired results?
We want to display the symbols of each involved object, plus the gene ID. This calls for:
- Gene.WormBase Gene ID
- Gene.Gene Name
- Gene (some relationship(s))-> Transcript.Sequence Name
- Gene (some relationship(s))-> CDS.Sequence Name
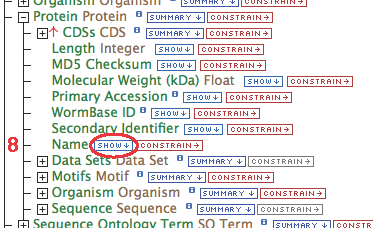
- Gene (some relationship(s))-> Protein.Name
Building the query
Click *SHOW* next to any of these field names to add that attribute to the resulting table as a column.
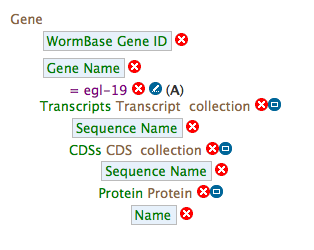
- Show the "WormBase Gene ID" and "Gene Name"
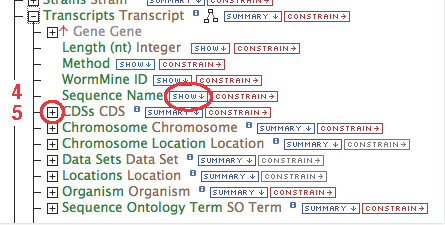
- Gene contains a collection of transcripts, this relationship represents transcription. Expand the relationship by clicking on the
[+]
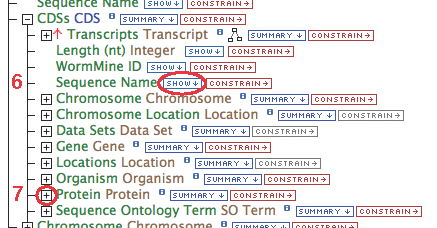
- Follow these steps for each of the data types in the chain as illustrated:
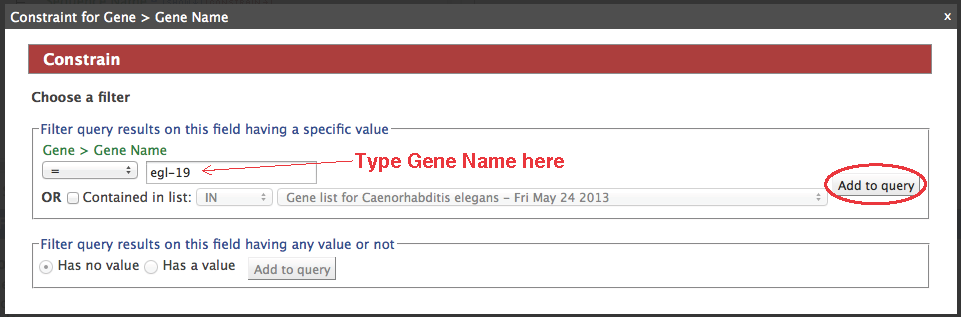
- Running the query at this point will give you results for all genes. If you have a smaller set in mind, like restricting the genes to egl-19 only, a constraint must be set.
- Click "constrain" next to the "Gene.Gene Name" field (circle #2), type "egl-19" in the text box, make sure the operator is "=", then "add to query".
- Your query overview should resemble this:
- Show results will execute the completed query.
constraining to a list
If you have access to any lists, the constraint dialog box will provide options with respect to them. Fields can be constrained such that their values must or mustn't be a member of that list.
Creating templates
Template queries are predefined (canned) queries. A template query can address a specific question and it can also be a good jump off point for refinements and for constructing queries that answer related questions. To create a template:
* Log in * Construct a query using Query Builder * Must include at least one constrain condition (e.g. restrict the format of the identifier) * "Start building a template query" * Fill in Name, Title and Description, and optionally comment * Make necessary adjustments, then "Save template" * Admin users can make a personal template public by My Mine -> Templates -> Add Tags -> New tag, type in the text box "im:public". Add one tag at a time. Tags help to group lists. For the list to be viewable by the Public, add a tag "im:public". For the list to be grouped under the "aspect" categories on the Home page, add the two tags: "im:frontpage" and "im:aspect:ACPECTNAME" The capitalisation of the ACPECTNAME that you use in the above tag is important. The word ASPECTNAME in the above tag should be replaced by one of Genomics, Proteins, Expression, Genetic Variations, Phenotypes, Gene Ontology, Strains Hit "Create". (This tag should be available for the next template you create). The Name field text should start with your initials to identify you as the author e.g. "XYZ Gene Homology" The Title field text is what the users see and should include '-->' which is converted into am arrow icon on the final template list on the Home page.
Creating lists
A list is a collection of identifiers of the same type of entities (e.g. genes, proteins, body parts). Lists can be compared and combined and be used as the starting points of queries. Sources of lists may be external (from a third party resource) or from WormMine. To generate a list and make it public:
1. Log in. 2. Make a query (Query Builder). 3. On the Result page, top right corner, select "Create / Add to List" -> "Create New List" -> "All of Columns ...", or "Choose individual items from the table". "Choose individual items from the table" allows further refinement. 4. Provide for the list: a Name, an informative Description, and Tags. The Name should start with your initials to identify you as the author e.g. "XYZ Gene Homology" 5. Descriptions and tags can also be edited after a list is saved.
Internal Report Page
find intermine internal id via a query (must be logged in as a super user)
http://206.108.125.166:8080/wormmine/report.do?id=
Other Sites
Tutorial on making templates http://www.yeastgenome.org/help/video-tutorials/yeastmine