Difference between revisions of "Worm numbers"
m (→Worm Volume) |
m (→Worm Volume) |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
| − | + | '''Volume of a single embryo''' = ~35 picoliters = ~0.000035 cubic millimeters = ~35,000 cubic microns | |
| − | + | '''Volume of a single L1 larva''' = ~80 picoliters = ~0.000080 cubic millimeters = ~80,000 cubic microns | |
| − | + | '''Volume of a single L2 larva''' = ~135 picoliters = ~0.000135 cubic millimeters = ~135,000 cubic microns | |
| − | + | '''Volume of a single L3 larva''' = ~300 picoliters = ~0.0003 cubic millimeters = ~300,000 cubic microns | |
| − | + | '''Volume of a single L4 larva''' = ~800 picoliters = ~0.0008 cubic millimeters = ~800,000 cubic microns | |
| − | + | '''Volume of a single Adult hermaphrodite''' = ~2.2 nanoliters = ~0.0022 cubic millimeters = ~2,200,000 cubic microns | |
Revision as of 19:19, 11 July 2012
This page is intended to become a collection ground for useful and interesting numbers about C. elegans biology. These numbers include things such as the average volume and mass (calculated estimates) of an adult hermaphrodite, larval stage, or embryo. Some of these numbers are well established facts whereas others are estimations, with a description of the method for calculating or estimating provided.
Worm Volume
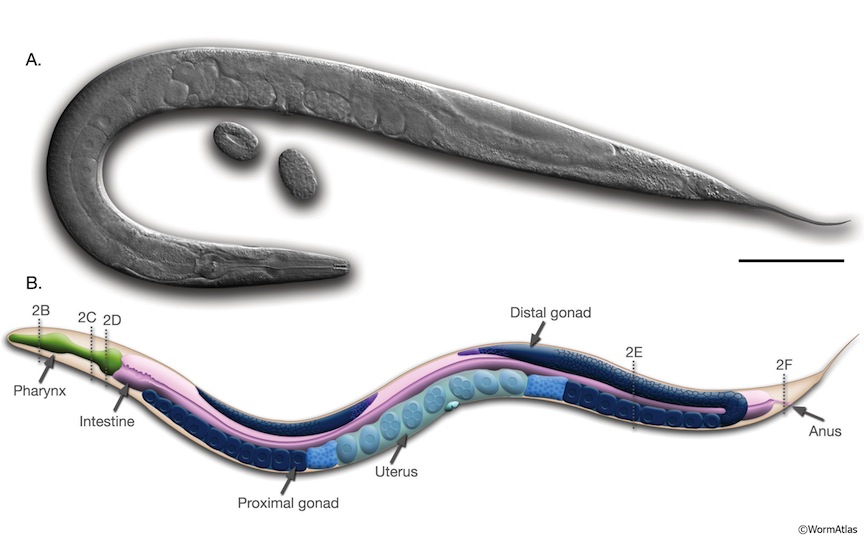
Based on these images from Worm Atlas (www.wormatlas.org):
... where the scale bar represents 100 microns, we can roughly deduce the volume of the embryo, each larval stage worm, and the adult hermaphrodite of C. elegans.
Volume of a single embryo = ~35 picoliters = ~0.000035 cubic millimeters = ~35,000 cubic microns
Volume of a single L1 larva = ~80 picoliters = ~0.000080 cubic millimeters = ~80,000 cubic microns
Volume of a single L2 larva = ~135 picoliters = ~0.000135 cubic millimeters = ~135,000 cubic microns
Volume of a single L3 larva = ~300 picoliters = ~0.0003 cubic millimeters = ~300,000 cubic microns
Volume of a single L4 larva = ~800 picoliters = ~0.0008 cubic millimeters = ~800,000 cubic microns
Volume of a single Adult hermaphrodite = ~2.2 nanoliters = ~0.0022 cubic millimeters = ~2,200,000 cubic microns
This paper (Lozano E. et al (2006) Curr Biol, [1]) finds wild type (N2) adult hermaphrodite worms growing to upwards of 6 nanoliters (0.006 cubic millimeters) [see Table 2, Figure 1A, and Figure 3 of paper].
Worm Mass
Assuming the worm has a density close to that of water (1 gram per milliliter) these are estimates of mass:
Single Embryo = ~35 nanograms
Single L1 larva = ~80 nanograms
Single L2 larva = ~135 nanograms
Single L3 larva = ~300 nanograms
Single L4 larva = ~800 nanograms
Single Adult hermaphrodite = ~2.2 micrograms
DNA Numbers
From the WS231 release notes of WormBase, the C. elegans genome has the following number of bases:
A 32,367,418
C 17,780,787
G 17,756,985
T 32,367,086
Total 100,272,276
This means that there are 35,537,772 GC base pairs (35.4% of the genome) and 64,734,504 AT base pairs (64.6% of the genome).
Genome Volume
Knowing that a single complete turn of DNA is approximately 3.4 nanometers in length (34 Ångstroms), 2 nanometers in width (20 Ångstroms), and is about 10 base pairs (bp)(and therefore 1 base pair is .34 nanometers long (3.4 Ångstroms)), we can deduce the volume of a single base pair of DNA to be roughly 1 cubic nanometer (1 nm^3):
Assuming a base pair is like a short cylinder with volume:
Volume = (pi)*(radius)^2*(height)
Volume = (~3.14)*(~1nm)^2*(~.34nm)
Volume of 1 base pair = ~1 cubic nanometer
Therefore:
No. of bp -> Volume
1bp -> 1 cubic nanometer
1kb -> 1000 cubic nanometers = 10^-6 cubic microns
1Mb -> 10^6 cubic nanometers = 10^-3 cubic microns
1Gb -> 10^9 cubic nanometers = 1 cubic micron
So, a single haploid genome of C. elegans (~100Mb) would be approximately 0.1 cubic microns and a diploid genome approximately 0.2 microns.
Packed into spheres, these would each be:
Volume of sphere = (4/3)*(pi)*(radius)^3
Haploid genome radius = ~0.29 microns
Haploid genome diameter = ~0.58 microns
Diploid genome radius = ~0.36 microns
Diploid genome diameter = ~0.72 microns
That is the smallest sphere that the haploid and diploid genomes, respectively, could pack into. We are, of course, ignoring proteins, RNA molecules, and any other small molecules, so the cell nuclei must be significantly larger. For polyploid nuclei, like those of the intestine, the nuclei must be substantially larger.
Genome Mass
Molar mass of dNMPs:
dAMP = 331.2 grams per mole
dCMP = 307.2 grams per mole
dGMP = 347.2 grams per mole
dTMP = 320.2 grams per mole
in polymer form (i.e. minus one water molecule, 18 grams per mole):
dAMP = 313.2 grams per mole
dCMP = 289.2 grams per mole
dGMP = 329.2 grams per mole
dTMP = 302.2 grams per mole
Average mass of polymer-dNMP = 308.5 grams per mole
An AT base pair = 615.4 grams per mole
A CG base pair = 618.4 grams per mole
The C. elegans haploid genome is ~100Mb (100,272,276 bp to be exact) with (as noted above) 35,537,772 GC base pairs and 64,734,504 AT base pairs, hence the total molar mass of the genome is:
[AT base pair molar mass]*[No. of AT base pairs] + [CG base pair molar mass]*[No. of CG base pairs]
(615.4g/mol)(64,734,504bp) + (618.4g/mol)(35,537,772bp) = 39,837,613,761.6 + 21,976,558,204.8
Molar mass of C. elegans genome = 61,814,171,966.4 grams per mole
Mass of C. elegans genome = 61,814,171,966.4 / Avagadro's number (6.022 * 10^23)
Mass of C. elegans genome = 103 * 10^-15 grams = 103 femtograms (fg)
There are 959 somatic nuclei in a single adult hermaphrodite, and so there are roughly 98.8 picograms of somatic genomic DNA that can be isolated from a single adult hermaphrodite, not including sperm, oocytes or other germline nuclei. This also does not account for the fact that some of the 959 somatic nuclei are polyploid, such as intestinal nuclei.